Rising companies usually rush to improve {hardware}, which ends up in stockpiling unused computer systems, routers, and different IT belongings. This follow could be a dangerous enterprise technique that results in worsening safety and environmental considerations.
Within the 2023 IT Administration Survey carried out by software program and IT companies agency Capterra, knowledge from 500 IT professionals at U.S. small and midsize companies (SMBs) exhibits that almost a 3rd (29%) interact in improper IT {hardware} disposal practices.
The analysis exhibits that SMBs usually hoard outdated computer systems for two.7 years earlier than grappling with what else to do with them. Even within the hybrid and distant work period, {hardware} pile-up stays an enormous a part of expertise’s ongoing transformation.
Key findings of the Capterra report present that almost all corporations recycle (80%), redeploy (65%), remarket (62%), or donate (54%) not less than a few of their IT {hardware} belongings. Nonetheless, many others resort to improper disposal that impacts negatively on the surroundings.
IT {hardware} units usually include poisonous chemical compounds that make them unsuitable for landfills or incinerators. These dangerous parts are probably devastating to the surroundings and folks.
“There are severe environmental, authorized, and regulatory implications of improper IT asset disposal, and companies ought to, due to this fact, prioritize accountable disposition processes,” supplied Zach Capers, senior safety analyst at Capterra.
Dysfunction Drives IT {Hardware} Dumping Disarray
The flexibility to prepare and stage IT belongings for disposal is a vital consider whether or not corporations use correct or improper disposal practices.
Value shouldn’t be. Dysfunction — not value — drives irresponsible disposition practices. Lack of group is a problem for 62% of SMBs inappropriately disposing of belongings, in comparison with 42% of accountable disposers.
Far too many merely throw away no longer-used {hardware}. The analysis exhibits that corporations partaking in irresponsible disposition practices usually tend to improve or substitute {hardware} to scale their workforce, keep away from obsolescence, and sustain with the competitors.
Alongside those self same strains, irresponsible disposers are considerably much less prone to reuse older units (54%) than accountable disposers (69%). Irresponsible disposers are inclined to have fewer complete {hardware} belongings but usually tend to lose observe of them.
Based on the report, in addition they are inclined to have fewer years in enterprise than corporations that get rid of their older {hardware} extra responsibly.
Organizations usually default to on-site storage or business trashing because of restricted consciousness of e-waste rules and the notion of comfort. Whereas the report emphasizes that dysfunction, not value, is the first driver of irresponsible disposition practices, Mark N. Vena, CEO and principal analyst at SmartTech Research, counters that value issues additionally play a job.
“Additionally, considerations about knowledge safety and potential breaches have prompted hesitation in adopting new disposal strategies. Value issues, lack of clear incentives for sustainable practices, and the absence of standardized processes additionally contribute,” he advised TechNewsWorld.
Accountable vs. Irresponsible Pc Gear Alternative
Understanding the associated fee issues units the stage for a deeper exploration into what differentiates accountable from irresponsible {hardware} disposal.
Capterra researchers have noticed varied methods corporations wrestle with organizing and staging their disposable belongings. One important discovering was that environmental impacts are an essential concern. Curiously, this concern seems to be motivated extra by guilt than by altruism.
For example, corporations that discard undesirable pc tools should usually confirm a sequence of custody, as {industry} rules continuously require. That may be a tougher process proposition for these corporations with organizing and staging points.
Then again, each teams share comparable struggles with the price of accountable disposal and discovering respected e-waste distributors. So irresponsible disposal practices can’t be blamed on both subject since each teams face them equally, in line with the report.
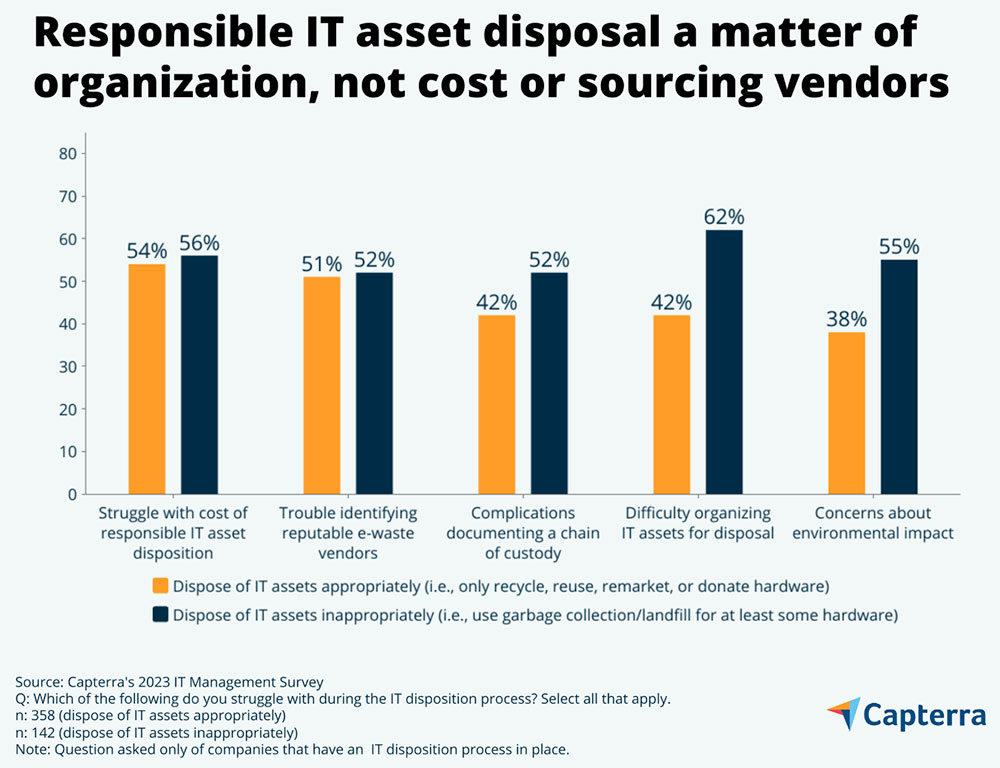
Moderately, these two points revolve round organizations deciding to take a straightforward — albeit unlawful — method out to empty their cluttered {hardware} storage closets. The opposite aspect of the conundrum finds corporations a number of years down the highway shedding chaos in favor of correct IT asset disposition processes, in line with Capterra.
The issue of IT {hardware} disposal is quickly escalating in significance, Vena famous. Technological developments result in shorter {hardware} lifespans, so the amount of discarded units is surging.
“Hanging a steadiness between sustainable disposal practices, knowledge safety, and compliance with evolving rules has develop into vital for organizations, governments, and society to handle the rising environmental and cybersecurity considerations,” he warned.
Going through Expensive Penalties
Based on Capterra, deciding to recycle IT belongings is barely step one. Corporations should nonetheless guarantee they full the handoff appropriately.
Environmental damages apart, irresponsibly disposing of IT belongings may end up in severe safety and authorized points. Some states have strict guidelines about throwing away sure IT tools and never safeguarding their digital contents.
Within the U.S., some states slap offenders with stiff penalties for violating native and federal privateness legal guidelines. Europe strictly enforces comparable rules. Additionally, within the U.S., companies should take care of {industry} rules like HIPAA, GLBA, and PCI-DSS. These all regulate the particular dealing with of delicate knowledge when decommissioning IT {hardware}.
Corporations should even be accountable when choosing established e-waste contractors with a confirmed compliance file with accountable knowledge destruction and e-waste requirements. Moreover, companies ought to take into account recycling packages by producers or retailers from which they bought their tools.
Some corporations prioritize cost-efficiency and comfort. Others would possibly lack consciousness concerning the potential environmental and safety dangers related to improper disposal, noticed Ron Edgerson, senior software safety marketing consultant at cybersecurity advisory companies agency Coalfire.
“The complexity of accountable disposal strategies, similar to digital waste recycling or hazardous materials remedy, can discourage organizations from adopting them,” he advised TechNewsWorld.
‘Gather and Dispose’ Scams Hamper Efforts
SMBs can too simply develop into interested in disposal scams, warned the Capterra report. All too frequent are corporations that gather fee whereas promising protected disposal. As a substitute, they ship the refuse to overseas nations or dump the {hardware} in poorly regulated landfills.
Edgerson added {that a} lack of acceptable disposal strategies exacerbates the IT disposal drawback, considerably impacting each the surroundings and knowledge safety.
“As consciousness of those points will increase, the significance of adopting sustainable and safe IT {hardware} disposal strategies turns into paramount to mitigate the potential penalties of this escalating drawback,” he stated.
Vena urged corporations can select licensed knowledge wiping companies and make use of strategies like degaussing or shredding to make sure knowledge eradication. Collaborating with e-waste recyclers that adhere to authorized frameworks and supply safe knowledge disposal is pivotal.
“This steadiness between sustainable disposal practices and knowledge safety is important for companies navigating fashionable compliance landscapes,” he stated.
Workable Choices Exist
SMBs and enormous enterprises have varied selections for disposing of enterprise-grade IT {hardware} aside from on-site storage or business trashing, continued Edgerson.
Recycling and refurbishment are ecologically pleasant strategies of extending the lifetime of the tools. Donating to non-profit organizations, colleges, or communities in want is one other worthwhile different.
“Selecting IT asset disposition (ITAD) corporations focusing on protected knowledge wiping and environmentally pleasant disposal procedures might give peace of thoughts whereas following authorized and moral norms,” he really helpful.
These selections not solely deal with {hardware} disposal issues. Additionally they adhere to sustainable practices and knowledge safety requirements, leading to extra accountable IT lifecycle administration, Edgerson famous.
The Want for Stepped-Up Laws and Enforcement
Given that almost one-third of corporations don’t promote or donate their discarded IT {hardware}, higher enforcement and regulation are in all probability one of the best resolution, concur Vena and Edgerson.
“That would encourage organizations to undertake extra accountable practices. This might in the end deal with each environmental considerations and knowledge safety points related to improper disposal of enterprise-grade IT {hardware},” supplied Vena.
Edgerson sees a holistic method involving enforcement and sufficient regulation as a viable resolution. Whereas enforcement instruments are essential in guaranteeing compliance, clear and well-defined legal guidelines set up the groundwork for enterprises to follow accountable disposal.
“By combining efficient enforcement, consciousness packages, and compliance incentives, corporations and the surroundings might profit from a extra sustainable and ecologically conscientious method to dealing with deserted {hardware} and waste,” he stated.
Trade Controls Alone Not Sufficient
Merely enhancing compliance help by way of cross-industry initiatives is unlikely to be sufficient. There’s a lack of standardization in self-regulation efforts throughout completely different sectors, and varied industries have differing ranges of authority when implementing {hardware} administration pointers.
“Some sectors, like well being care and finance, face stringent rules because of delicate knowledge considerations. In distinction, industries with much less regulatory oversight might need extra flexibility,” defined Edgerson. “Nonetheless, as environmental and knowledge safety consciousness grows, industry-led initiatives and requirements are rising.”
Industries can affect their members. However complete and constant rules from authorities our bodies stay essential to making sure accountable and uniform {hardware} disposal practices throughout sectors, he concluded.
Vena agreed that strengthening state and federal disposal rules may certainly be a viable resolution.
“This might in the end deal with each environmental considerations and knowledge safety points related to improper disposal of enterprise-grade IT {hardware},” he stated.




Discussion about this post